Inflammation is at the center of everything in the body, from sore muscles to autoimmune diseases. They are signs that tell us our health is at risk and where help is needed. Both a lifesaver and a killer, inflammation is to be taken seriously and treated in the correct manner. So how does Cannabis fit into this dynamic?
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation
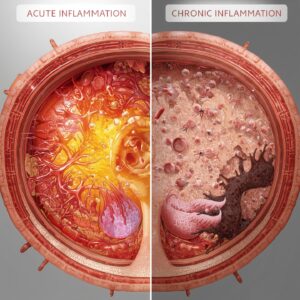
Acute Inflammation
Characterized by a few simple causes and symptoms. Acute inflammation occurs within minutes or hours of the causing incident. The purpose is to eliminate or prevent the spread of pathogens, to remove necrotic cells/tissue and to start a repair process. Caused by injury, infection or internal issues.
Your easy-to-see symptoms will be pain, redness, immobility, swelling and heat/fever. The sign of it being acute means that it doesn’t last more than two weeks. The inflammation can be known or unknown. Injury being a known as you’re aware when it happens and flu being unknown as it takes time to see symptoms.
Chronic Inflammation
Characterized by the same symptoms of acute inflammation except usually intensified and can last a lifetime. Causes are often more severe and extensive. Features like:
Ongoing tissue destruction
Attempts to repair with fibrosis
They can develop from acute causes or be insidious in onset. Things like fungi, syphilis, tuberculosis, parasites and leprosy, these are just examples of what chronic inflammation comes from.
So Where Can Cannabis Help
Acute Inflammation
THC and CBD both interact with the ECS (endocannabinoid system), a system that helps regulate inflammation, pain and immune response. Mainly CBD interacts with the CB2 receptors which reduce pain perception, inflammation and swelling.
Think sprained ankle, dental pain, or post-surgery irritation. Cannabis may ease the discomfort but won’t replace medical treatment. Athletes sometimes use CBD topicals post-training to reduce short-term inflammation in muscles and joints.
- Chronic Inflammation
Often comes with persistent pain (arthritis, fibromyalgia). Cannabis compounds act on CB1 (nervous system) and CB2 (immune cells) receptors, lowering pain perception and calming inflammatory processes. - Conditions like multiple sclerosis, Crohn’s, lupus involve the immune system attacking the body. Cannabis can tone down excessive immune activation, reducing flare-up intensity.
- Chronic inflammation in the brain (microglial activation) is linked to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. CBD shows potential in reducing this “smoldering” inflammation, possibly slowing progression.
Where Cannabis Doesn’t Help
- Acute Inflammation
Cannabis does a good job in minor fixes and regulates pain on a small scale. Although there are alternative solutions that work more efficiently. Fast pain relief is important in many cases, and strong anti-inflammatories that reduce swelling within a short period of time like ibuprofen. - Cannabis solutions are minor and slow. Often healthier than many other drugs that give people stomach ulcers and affect the liver & pancreas negatively. Cannabis doesn’t help when it hides symptoms that need to be seen, such as in cases of flu, it will also lower the immune system.
- The other obvious factor is the addiction that can come with it. CBD should be the main medicine that is taken for cases in which it will work. Whereas THC can become addictive and has fewer healing properties in this sector.
Ways of Consumption: Cause or Cure Depends on the Method
1. Smoking
The most traditional method, yet also the harshest. While smoking delivers cannabinoids quickly, it also introduces heat and combustion by-products like tar, which can irritate lung tissue and trigger inflammation. The dose is often too low as well, unless distillate vapes are being used.
Pros: Fast-acting, easy to dose.
Cons: Lung irritation, pro-inflammatory side effects.
2. Vaping
A cleaner alternative to smoking that heats cannabis without burning it. This reduces exposure to harmful toxins, though long-term effects are still debated.
Pros: Lower lung irritation, fast onset.
Cons: Quality varies by device/oil, long-term safety still unclear.
3. Edibles
Ingested cannabis is processed through the liver, producing a slower but longer-lasting effect. For inflammation, this offers sustained relief, but dosing can be tricky. You also can’t forget the ingredients that go into the edible (oil, butter, sugar, flour). These products negatively affect types of inflammation.
Pros: Long-lasting effects, no lung damage.
Cons: Delayed onset, risk of overconsumption.
4. Oils & Tinctures
Taken under the tongue or mixed with food, oils offer a balance between smoking and edibles. They’re discreet, versatile, and avoid combustion altogether. This is the correct medical way to consume cannabis for its healing properties.
Pros: Precise dosing, clean method, moderate duration.
Cons: Slower onset than smoking/vaping, quality depends on extraction process.
Conclusion: Cause, Cure or Confusion
The reality is that it’s all the above. This is a very case-specific drug, not like painkillers or anti-inflammatory pills you can buy behind the counter at the chemist. One must consult their doctor or practitioner to be certain if cannabis is the correct temporary or long-term solution for them.
Cannabis doesn’t cure anything according to our current studies. Although it does make life considerably easier in many cases and slows down the speed at which our health problems consume us. Always seek medical advice. The information you see in this post is not medical advice.
